FRAGMENT REPLACEMENT & MOLECULAR DESIGN
BROOD
BROOD is designed to help explore chemical and property space around a hit or lead molecule. BROOD generates analogs of the lead by replacing selected fragments in the molecule with fragments that have similar shape and electrostatics, yet with selectively modified molecular properties.
BROOD fragment searching has multiple applications, including lead-hopping, side-chain enumeration, patent breaking, fragment merging, property manipulation, and patent protection by SAR expansion.
Using OpenEye’s BROOD software for scaffold hopping, we successfully discovered a new chemical series from our lead compound, with equipotency and improved stability. – Laurent D., Lundbeck
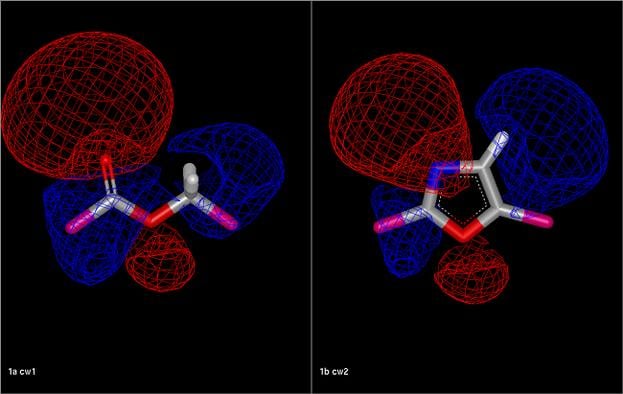
Comparison of an ester fragment and an oxazole fragment showing the electrostatic isopotential contour surfaces. The electrostatic Tanimoto between the two fragments is 0.54.
Features
- Graphical query editing including the ability to easily modify the similarity force-field as well as add and remove chemical constraints such as those known to be critical to the SAR under development
- Graphical interface to facilitate physical property analysis and real-time property filtering of millions of potential molecules
- Integrated estimation of synthetic accessibility
- Construction and assessment of new molecule series in a protein active-site
- Hierarchical organization of the hitlist of analog molecules along with a new graphical interface designed specifically to explore and edit the hitlists
- Database of more than 4 million medicinally relevant fragments provided and utilities to aid users in augmenting this database with novel fragments from their corporate collections
- Tools for modelers and chemists to communicate their ideas and preferences including favorite molecules list management, molecular annotation, view bookmarking and hitlist subsetting
ROCS X: AI-Enabled Molecular Search Unlocks Trillions
Webinar: OpenEye's Free energy prediction for drug discovery: Ideas at breakfast, discoveries by lunch
Science Brief: Binding Free Energy Redefined: Accurate, Fast, Affordable
CUP XXV - Santa Fe March 10-12, 2026
Webinar: Novel Hits from Beyond the Known: ROCS X
Webinar: OpenEye's Free energy prediction for drug discovery: Ideas at breakfast, discoveries by lunch
Science Brief: Binding Free Energy Redefined: Accurate, Fast, Affordable
CUP XXV - Santa Fe March 10-12, 2026
Webinar: Novel Hits from Beyond the Known: ROCS X
Resources
Glimpse the Future through News, Events, Webinars and more
News
ROCS X: AI-Enabled Molecular Search Unlocks Trillions
BOSTON, OpenEye miniCUP—Sept. 25, 2025—Cadence Molecular Sciences (OpenEye), a business unit of Cadence (Nasdaq: CDNS), announced today at miniCUP Boston, the launch of ROCS X, an AI-enabled virtual screening solution that allows scientists to conduct 3D searches of trillions of drug-like molecules.
Read now
Webinar
Webinar: OpenEye's Free energy prediction for drug discovery: Ideas at breakfast, discoveries by lunch
Webinar: OpenEye's Free energy prediction for drug discovery: Ideas at breakfast, discoveries by lunch We are continuing our 2025 miniWEBINAR series with our November session led by Chris Neale, Ph.D., who leads the molecular binding affinity solution group at OpenEye, Cadence Molecular Sciences. His expertise and interests include method development for structure-based drug design, cellular signal transduction, and uncertainty quantification. Chris is also an editorial board member at the Biophysical Journal.
Read now


