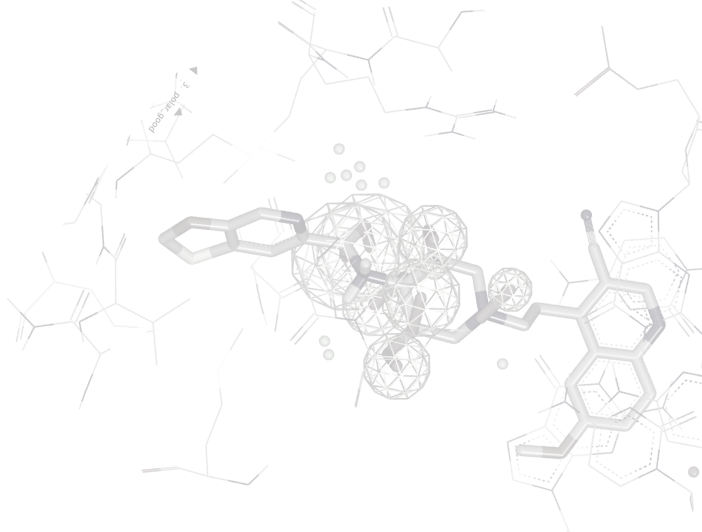
ROCS - Shape Similarity
ROCS® is powerful ligand-based lead discovery software that identifies potentially active leads by comparing molecules using shape and the distribution of chemical features, or color. Screening of databases can be carried out at hundreds of molecules per second on a single CPU, allowing rapid analysis of large collections of molecules. ROCS is competitive with, and often superior to, structure-based approaches in virtual screening [1,2], both in terms of overall performance and consistency [3]. Novel and interesting molecular scaffolds have been identified using ROCS against targets often considered very difficult for computational techniques to address [4].
ROCS and its graphics processing unit implementation FastROCS are industry standards that have been applied in many published and unpublished inhibitor discovery efforts over the past 20 years. --Correy et al. (Sci. Adv. 2025)

Features
- Returns overlays based on matching both 3D shape and chemistry
- Processes hundreds of compounds per second on a single CPU
- Overlays are intuitive and visually informative when viewed in standard visualizers (e.g. VIDA)
- Feature matching based on user-definable color force-fields
- Query shape may be a molecule, a grid (e.g. electron density, active site, or arbitrary volume) or a composite of the two
- Intuitive graphical user interface with a query editor and statistical tools for query validation
- Distributed processing via MPI for all supported platforms
ROCS is the class-leading shape comparison application; it has been used successfully in hundreds of published studies to find new chemical matter with relevant biology. It uses a smooth Gaussian function to represent the molecular volume [5], so it is possible to routinely minimize to the best global match.
ROCS features include shape and color overlay, optimized overlays for queries composed solely of color atoms or Gaussians, and support for using grids as database entities for overlay.

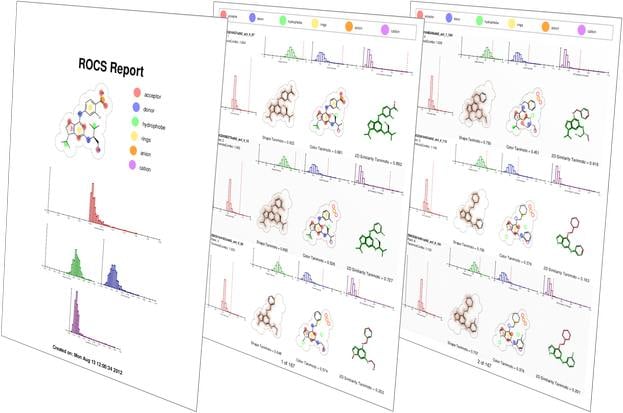
ROCS alignments have a number of applications: 3D-QSAR, SAR analysis, understanding of scaffold diversity and detection of common binding elements[6]. ROCS alignments to crystallographic conformations have also been useful in pose prediction in the absence of a protein structure [7].
vROCS is the graphical user interface for ROCS that enables users to jump right into working with ROCS. vROCS also provides a powerful query editor enabling the advanced user to design complex queries. Recognizing the importance of query validation, vROCS includes a collection of statistical tools to evaluate the performance of different queries.
For more detailed information on ROCS, check out the link below:
DocumentationYou may also be interested in:
FastROCS and FastROCS Plus
FastROCS is a GPU-accelerated shape similarity search tool. FastROCS Plus extends FastROCS by incorporating consensus scoring with high-speed docking, seamlessly combining ligand- and structure-based approaches in a single step.
ROCS X
ROCS X performs virtual screening at the trillion-compound scale. Rapidly identify relevant, synthesizable molecules without the need to enumerate them all.
Learn more
Download OpenEye Science Brief on Searching in synthon-based chemical space using shape similarity as the ranking criteria with Shape-Aware Synthon Search (SASS)
For science details and application examples, WATCH OpenEye’s miniWebinar recording from Spetember 2023 on ROCS: Solutions with Molecular Shape by Paul Hawkins, Ph.D., Product Evangelist, OpenEye, Cadence Molecular Sciences.
References
- Comparison of Shape-Matching and Docking as Virtual Screening Tools Hawkins, P.C.D., Skillman, A.G., Nicholls, A., J. Med. Chem., 2007, 50, 74.
- Assessment of Scaffold Hopping Efficiency by Use of Molecular Interaction Fingerprints Venhorst, J., Nunez, S., Terpstra, J.W., Kruse, C.G., J. Med. Chem., 2008, 51, 3222.
- Multiple protein structures and multiple ligands: effects on the apparent goodness of virtual screening results Sheridan, R.P., McGaughey, G.B., Cornell, W.D., J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des., 2008, 22, 257.
- A Shape-Based 3-D Scaffold Hopping Method and Its Application to a Bacterial Protein−Protein Interaction Rush, T.S., Grant, J.A., Mosyak, L., Nicholls, A., J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48, 1489.
- A fast method of molecular shape comparison: A simple application of a Gaussian description of molecular shape Grant, J.A., Gallardo, M.A., Pickup, B., J. Comp. Chem., 1996, 17, 1653.
- Multitemplate Alignment Method for the Development of a Reliable 3D-QSAR Model for the Analysis of MMP3 Inhibitors Tuccinardi, T., Ortore, G., Amelia Santos, M., Marques, S. M., Nuti, E., Rosello, A., Martinelli, A. J. Chem., Inf. Model, 2007, 47, 2293.
- Lessons in Molecular Recognition. 2. Assessing and Improving Cross-Docking Accuracy Sutherland, J.J., Nandigam, R.K., Erickson, J.A., Vieth, M. J. Chem., Inf. Model, 2007, 49, 1715.
Webinar: OpenEye's Free energy prediction for drug discovery: Ideas at breakfast, discoveries by lunch
Science Brief: Binding Free Energy Redefined: Accurate, Fast, Affordable
CUP XXV - Santa Fe March 10-12, 2026
Webinar: Novel Hits from Beyond the Known: ROCS X
Resources
Glimpse the Future through News, Events, Webinars and more
News
ROCS X: AI-Enabled Molecular Search Unlocks Trillions
Webinar
Webinar: OpenEye's Free energy prediction for drug discovery: Ideas at breakfast, discoveries by lunch


